
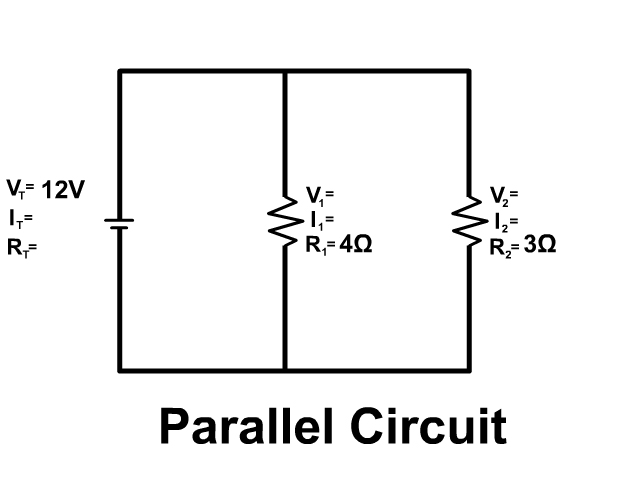
This means that the overall resistance has decreased in the circuit. The more resistors we add in parallel, the more ‘pathways’ the current has to go through, so it is easier for current to flow through the circuit. The potential difference is the same in every single component in the circuit. In a parallel circuit, adding resistors will decrease the resistance. Resistors in parallel decrease resistance.The more resistors added, the harder it is for current to flow.
Parallel circuit definition series#
This means that the overall resistance has increased in a series circuit. The current is the same in every single component in the circuit, so the more resistors we add, the harder it is for current to flow. In a series circuit, adding resistors will increase resistance.

In other words, the total current through the whole circuit is the sum of the currents through the separate components. The sum of the currents of all branches is equal to the total current that flows from the cell / battery. The current is split between the branches of the circuit.This means more components may be added in parallel without needing extra voltage. Therefore bulbs in parallel will have the same brightness (assuming equal resistance). In parallel circuits, every single component gets the full, maximum voltage. In series circuits the voltage was shared between the components (in proportion of their resistance). The voltage is the same for all components. Series and Parallel Circuits Parallel Circuits However, this means that if one light breaks then they all break. Christmas lights are often sometimes in series circuits, because each bulb only needs a small voltage, so it is better to share the voltage in series. There is only one route for charge, so if one lamp in a series circuit is broken, all lamps will stop working. A break in one component ruins the whole circuit.If there are two cells or batteries, then the voltage from both add up together to give the total circuit voltage. We can use the following equation to work out the total resistance in a series circuit: Therefore if you add an extra lamp to a series circuit, the total resistance increases and hence the current decreases. Current needs to be the same everywhere, so the higher the resistance of an individual component, the greater its share of the voltage (so that current, which is voltage / resistance, stays equal). Total resistance is the sum of the resistances of all components.The total voltage from the battery / cell is shared between the components – if the battery or cell provides 5V of energy, and there are two lamps (with equal resistance), each lamp will get 2.5V. Total voltage is shared amongst components.You can calculate the current by dividing the total voltage of the battery or cell by the total resistance in the circuit. Current is not ‘used up’ along the circuit, so remains constant. Current is the same in all parts of the circuit.There are a few rules and facts about series circuits that we need to remember.
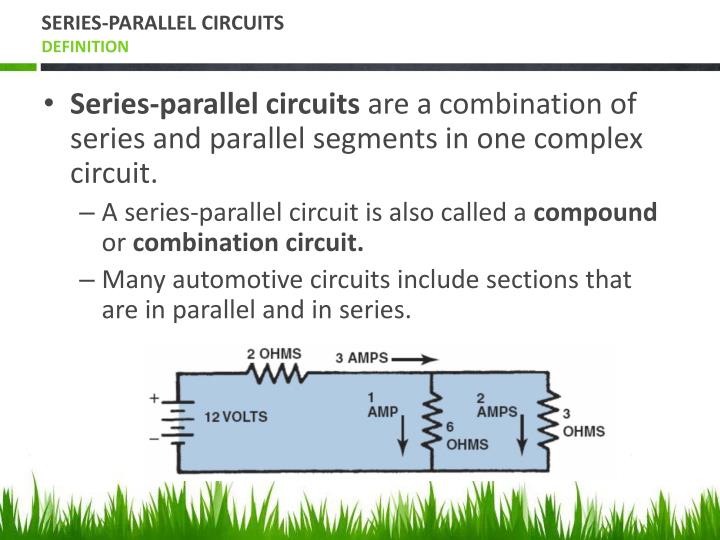
Series and Parallel Circuits Series and Parallel Circuits Series Circuits Some circuits can have both series and parallel parts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
